Understand Liver Cancer Symptoms, Treatment & Stages
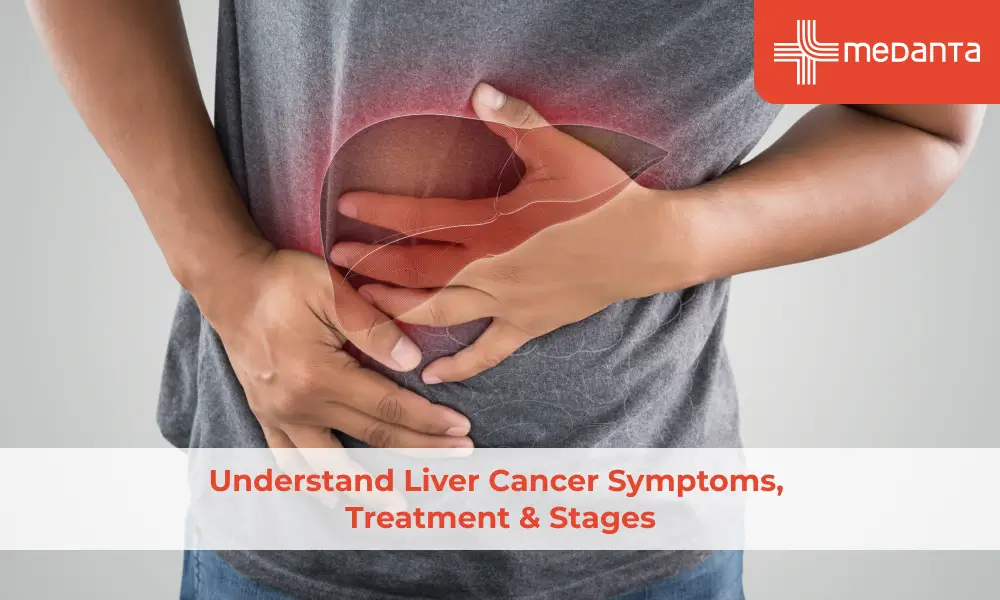
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Liver cancer is a disease that affects the cells of the liver and happens when abnormal cells grow at a rapid pace and leave insufficient space for normal cells. The liver is located beneath the rib cage in the upper right portion of the abdomen and is the largest solid organ in the body. Various types of cancer affect the liver and are classified as primary and secondary liver cancer.
Primary liver cancer originates in the tissue of the liver. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer and it begins by affecting the hepatocyte liver cells, whereas intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma are relatively less common types of liver cancer.
Cancer that starts in another region of the body, such as the lung, breast, or colon, and then spreads to the liver is known as secondary liver cancer. This type of cancer, also known as metastatic liver cancer, is as common as primary cancer.
What Is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow rapidly in the liver, affecting its ability to function. It is categorized into primary liver cancer and secondary (metastatic) liver cancer, based on where it originates.
Key Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
There are several conditions that increase the risk of developing liver cancer. A risk factor does not necessarily mean that a person will contract that disease; rather, it is an indicator that the chances of being diagnosed with a particular disease are higher due to certain factors. A cancer specialist can help guide at-risk patients with regular check-ups.
For liver cancer the some of the following risk factors are a concern:
Family history of liver diseases
Ailing from other liver diseases like Cirrhosis, Hepatitis B or C
Suffering from diabetes
Suffering from obesity
Gender plays a role as men are more likely to develop liver cancer than women.
Alcoholism or too much consumption of alcohol over a long period of time
Liver Cancer Symptoms You Shouldn't Ignore
Liver cancer in its early stages generally does not display any significant signs or symptoms. Once the liver becomes swollen, some of the following symptoms might become noticeable:
Unexplained weight loss
Nausea
Pain near the right shoulder
Pain on the right side of the abdomen
Presence of lump below the rib cage
Loss of appetite
Fatigue
Bloating
Dark yellow urine
Jaundice
It is recommended to visit a cancer specialist in the country’s best cancer hospitals once such symptoms are noticed.
How Is Liver Cancer Diagnosed?
When a cancer specialist detects a lump or finds other symptoms that are indicative of liver cancer, they may run tests to confirm their diagnosis. Tests and procedures used to detect liver cancer include:
Blood Tests: Blood tests are used to detect any abnormalities in liver function.
Imaging Tests: A cancer specialist may want to order imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scan or MRI to gain better and detailed images of the affected organ.
Biopsy: A biopsy is the most reliable way to confirm a liver cancer diagnosis. In this method, a piece of liver tissue is extracted from the body and sent for laboratory testing. This piece is then observed under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Liver biopsy can sometimes lead to bleeding, bruising, or infection, so it is advisable to get it done at the best cancer hospitals.
Stages of Liver Cancer: From Stage 1 to Stage 4
There are four stages of liver cancer and the doctor assigns a number from one to four depending on the stage at which the cancer has been detected. The higher the number, the more the cancer has spread and treatment options are decided accordingly. The four stages of liver cancer are as follows:
Stage I: This stage means that only a single tumour has been detected in the liver and no other organs have been affected.
Stage II: In this stage, a single tumour is found, but the disease has also spread to the blood vessels. Stage two might also indicate that more than one tumour has been detected but they are less than 3 cm in size.
Stage III: In Stage three liver cancer, multiple tumours are detected and at least one of them is larger than 5 cm. Stage three liver cancer can also be declared when the cancer has spread beyond the liver and affected large blood vessels, other organs or lymph nodes.
Stage IV: Stage four cancer is almost impossible to cure and indicates that the cancer has spread to multiple places in the body and affected body parts and organs such as the lungs, bones, lymph nodes and so on.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer
For treatment of liver cancer, there are various doctors and cancer specialists who can be consulted. Treatment options are determined by a number of factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient's age and expected life span, other health issues, the need for surgical intervention, potential side effects, and so on. In Medanta, based on the situation, a team of doctors and specialists like surgical oncologists, gastroenterologist, radiation oncologist, interventional radiologist and other health professionals are chosen to provide expert treatment and care. Best cancer hospitals ensure that the treatment plan and team of doctors chosen come up with a comprehensive treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs and expectations. The following types of treatments are available to help a patient deal with liver cancer.
TREATMENTS
Partial hepatectomy: This process involves using surgery to remove the liver cancer and a portion of healthy liver tissue surrounding the tumour. A partial hepatectomy depends on liver function, overall health, size and location of the tumour within the liver.
Total hepatectomy and liver transplant: This surgery involves removing the whole liver and replacing it with another liver received from a donor. A liver transplant is viable only if the cancer has been detected at an early stage and a healthy liver is available. Thus, this option can be exercised for a small number of people with early-stage liver cancer.
OTHER TREATMENTS
Ablation therapy: This therapy is used to treat and destroy cancer cells in the liver without surgical intervention. There are various types of ablation that may be used depending on the situation, like microwave ablation, which uses electromagnetic methods, and ethanol ablation, wherein pure alcohol is injected directly into the tumour. Cryo ablation, which involves using extreme cold to destroy cancer cells, and radiofrequency ablation, which makes use of electric current that heats and destroys cancer cells,
Chemotherapy: Chemoembolization is a type of chemotherapy treatment that uses anti-cancer drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from multiplying further. They are administered directly to the liver. There are other chemotherapy options that use pills or injections that circulate throughout the body as well.
Targeted therapy: In this therapy, drug treatments are used to target specific abnormalities within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, cancer cells begin to die. These therapies may work only for people with certain genetic mutations.
Immunotherapy: This process uses the immune system to fight cancer and is generally used for people diagnosed with advanced liver cancer. It is done by using drugs that direct the body’s immune system to kill cancer cells.
Radiation therapy: This treatment uses sources such as X-rays and protons that are high in energy to destroy cancer cells. This shrinks tumours and can help deal with and control symptoms in advanced stages of liver cancer.
Loco-regional therapy: Radio embolization is a type of therapy where tiny beads that contain radiation are placed into the liver to deliver radiation directly to the tumour. Another type of therapy that may be used is called chemoembolization, where chemotherapy drugs are combined with the beads to block the hepatic artery.






