The Benefits of ECMO in Heart Failure Patients

When someone’s heart and lungs stop working efficiently and become too weak to function on their own, an advanced therapy called extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is used. In essence, it is a device that replaces the functions of the heart and lungs, adding oxygen to the patient's blood and eliminating carbon dioxide.
ECMO for heart failure devices offers long-term heart support for hours, days, or even weeks to give a patient's heart enough time to recover and restore function. This is in contrast to heart-lung bypass machines, which are intended for short-term usage, such as during heart surgery. The Extracorporeal Life Support Organization data shows that over 15,000 adult patients have received VA-ECMO since 1990, with a roughly 40% ECMO survival rates till hospital discharge.
What is ECMO?
Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation is referred to as ECMO, however, ECLS, which stands for Extra Corporeal Life Support, is another name for it. ECMO involves supporting a patient's heart and/or lungs, and after continually pumping blood out of your body, ECMO passes it via machines that remove carbon dioxide and supply oxygen to the blood. The blood is subsequently pumped back into your body, and that is how ECMO may sustain the body for a few days or even months. You need to remember, ECMO is merely a form of support; it is not a permanent cure in the form of steady intervention.
Patients of all ages, from newborns to adults, can benefit from ECMO, and it can help patients with a variety of serious heart and lung disorders from respiratory failure to cardiac arrest. However, remember that ECMO therapy is often reserved for situations in which the underlying heart or lung conditions have not been resolved by any other conventional treatment.
There are two varieties of ECMO - Venoarterial (VA) ECMO and Venovenous (VV) ECMO.
- Venoarterial (VA) ECMO - The VA ECMO is attached to both a vein and an artery and is used when a patient has issues with both their heart and lungs.
- Venovenous (VV) ECMO - A VV ECMO on the other hand is attached to one or more of the veins, often close to the heart, when the problem solely affects the lungs.
In order to give ECMO assistance in emergency situations, hospitals use smaller portable ECMO equipment that is lightweight enough to be carried by one person and transportable in an ambulance, and this can save lives.
What is the Work Process of an ECMO?
First of all, surgery is required to connect a patient to the ECMO machine, and plastic tubes known as cannulas are used to link the ECMO machine to the patient. The doctor inserts cannulas into the patient's big arteries and veins in the legs, neck, or chest. They do it after administering an anticoagulant, a drug that stops blood from clotting.
After this process, the patient's blood is drawn by the ECMO system, through cannulas and into an artificial lung membrane oxygenator to remove carbon dioxide and provide oxygen to the blood. This treated blood is then pumped back into the patient by the ECMO system after being warmed to body temperature. This blood is pumped through the patient's circulatory system by a mechanical pump when the patient's heart is unable to pump blood effectively!
To make patients as comfortable and pain-free as possible, surgeons continue to give sedatives and painkillers during and after the treatment, and regular chest X-rays will be performed by an ECMO team of physicians, nurses, and other medical professionals. This helps physicians assess and monitor the patient's heart and lung health, and in order to measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels and look for any illnesses, the team will also do routine blood tests.
Benefits of ECMO in Heart Failure Patients
ECMO is particularly beneficial for heart failure patients and can save lives when used without delay!
- Cardiogenic Shock
A heart attack or serious heart failure often results in the development of a medical disease called cardiogenic shock where the heart is unable to pump blood quickly enough to meet the body's demands. ECMO can greatly help in this situation and physicians who have access to this machine are often able to successfully treat the patient.
- Heart Injuries
If you have cardiac damage from trauma or other illnesses, that may cause a heart attack, you could require ECMO treatment! One of the main ECMO advantages is that it can treat heart attacks efficiently. ECMO is also frequently used to treat newborns and infants with heart issues, particularly those born prematurely.
Other Conditions that ECMO can Treat
Although there isn't a set list of ailments for which ECMO is prescribed, physicians may advise using it in the following circumstances:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome or ARDS
- Heart transplant
- Lung transplant
- Pulmonary embolism
- Respiratory failure
- Pneumoniqs (HINI, Swineflu, Covid-19)
- Poisonings
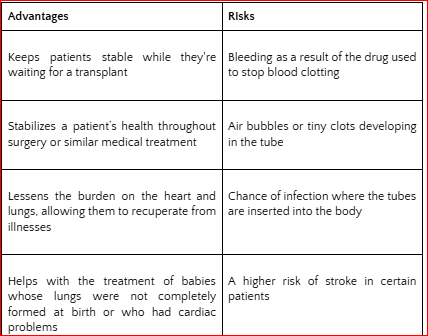
Advantages of Using an ECMO Machine
By offering prompt and effective support for both cardiac and respiratory functions, ECMO guarantees vital oxygenation and circulation even in the most severe cases of heart or lung failure. In critical care settings, the ECMO method is a helpful therapy because of its several advantages, so let’s take a look.
- ECMO reduces ventilator-induced lung damage and allows the lungs to heal
- Helps babies with heart issues or undeveloped lungs at birth
- Keeps a patient alive while undergoing surgery or other medical procedures
ECMO has the potential to save lives by providing patients with the vital support they require as they await an organ transplant or recuperate from diseases
Generally speaking, physicians want to remove patients from ECMO treatment as soon as feasible, but the duration of ECMO therapy can vary significantly since it is used for patients with a variety of diseases, each of which has a unique recovery schedule. While some patients may need ECMO support for days or weeks, others may just need it for a few hours, so the ECMO team will start the weaning procedure as soon as the patient reaches a stage where the ECMO machine is no longer required.
The ECMO machine will not be shut off completely at first, instead, the team conducts a trial (known as a weaning trial) during which they gradually reduce the patient's blood supply via the device for precaution. They monitor the patient's reaction to this decrease in ECMO assistance over a period of several hours, and a surgeon will remove the cannulas if the patient reacts well and the ECMO team determines that stopping ECMO is safe.
A patient may need a ventilator to maintain their breathing after ECMO support gets removed and doctors will take the ventilator off the patient as soon as they can breathe on their own. However, unless vital signs stabilize, ECMO therapy heart patients might still need to stay in the hospital for a few days or weeks! What’s more, following prolonged use of a ventilator's breathing tube, many may also require speech therapy to promote speech rehabilitation and physical therapy to assist rebuild muscular strength to normal.
Final Remarks
Severely sick patients with heart or lung issues may greatly benefit from ECMO! Even though the use of this machine is not exactly new, modern medicine now knows more than ever before how ECMO may save lives! However, it isn't safe to use on everyone, so consulting with a doctor first before opting for this treatment is a must.
To consult with the top heart specialists in India, contact Medanta today and book an appointment!






