Monitoring Foetal Growth: Ensuring a Healthy Pregnancy

After conception, the embryo is created, and then it undergoes several changes as it develops from a single cell into a fully-formed healthy baby. Pregnancy is typically a nine-month process, and the baby's nervous system, limbs, and internal organs, all grow throughout this period. However, the nine-month number isn't always the case, rather, forty weeks, or two hundred and eighty days, is the length of a full-term pregnancy.
Over the course of a normal pregnancy, the fetus will undergo significant changes, and the three phases of this foetal growth period are referred to as trimesters. Every trimester lasts around three months, and the baby’s development is measured throughout this time to ensure that the baby is healthy! In 2020, India's infant mortality rate (IMR) was 28 per 1,000 live births, however, with proper care and regular fetal growth checks, this number can be decreased further.
What are the Fetal Development Stages?
The process of fetal development starts before you are even aware that you are pregnant! There are several intricate procedures that happen between conception and delivery, and this process is divided into stages. There are a total of three foetal development stages called the germinal stage, embryonic stage, and fetal stage.
- Germinal stage
The shortest stage of foetal development is called the germinal stage, which begins when an egg and sperm unite in your fallopian tube during conception. After fertilizing the egg, the sperm produces a zygote, and over the course of around a week, the zygote starts its journey to your uterus. The zygote undergoes several divisions throughout this process, ultimately becoming two distinct structures constructive the embryo, which will eventually become the fetus, while the other structure developing into placenta develops from the other. Cells continue to divide quickly during this entire time, and the zygote eventually develops into a blastocyst. Once within your uterus, the blastocyst installs itself in the lining of your uterus, and your body instantly starts generating hormones to sustain a pregnancy if implantation is successful. Additionally, this ends your menstrual cycle until the pregnancy has ended.
- Embryonic stage
From around the third week of pregnancy until the end of the eighth week, the embryonic stage lasts, and during this stage, the blastocyst starts to exhibit recognizable human features. Now it is referred to as an embryo, and the neural tube, which eventually creates the brain and spinal cord, and the skull, eyes, mouth, and limbs are among the structures and organs that keep developing. Around five to six weeks in a healthy pregnancy, the cells that will make up the fetal heart start to group and get the ability to beat. Around the sixth week, the sections that will grow into limbs and legs also begin to develop, and the majority of the embryo's systems and organs begin to take shape by the end of the eighth week.
- Fetal stage
Around the ninth week, the embryo formally becomes a fetus, and the fetal stage of development starts, which continues until delivery. Although it is not yet visible on ultrasound, the fetus receives its assigned sex around week nine of pregnancy, while the main bodily systems and organs of the fetus keep developing and growing. Additionally, hair, eyelashes, and fingernails develop, and even though you might not see it until twenty weeks of pregnancy, the fetus can move its limbs because most of the weight and length growth occurs during the fetal stage.
Fetal Growth Chart
In these foetal growth charts, we have mentioned the fetal growth parameters that apply in a healthy pregnancy between eight weeks to forty one weeks.
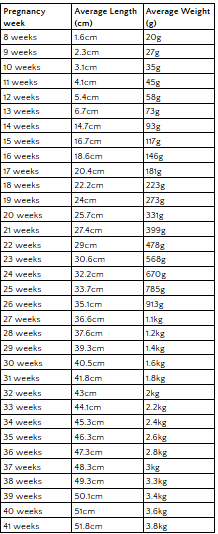
Fetal growth monitoring makes sure the baby is receiving all the nourishment it needs, which is essential for growth, however, other issues too can be handled properly when regular checkup is done.
- Early Identification of Fetal Abnormality
Frequent evaluations assist in the identification of various fetal structure defects and fetal growth problems or other developmental abnormalities.
- Prenatal Treatment
Healthcare professionals can customize prenatal treatment to fit the specific requirements of the mother and the unborn child by monitoring fetal development.
What are the Techniques to Check for Fetal Growth?
1. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is one of the most common foetal growth assessment techniques used practically everywhere and for every pregnant woman! This essential tool offers comprehensive pictures of the fetus dimensions, morphology, general health, the baby's location in the womb, and gestational age. Fetal biometry determines a fetus's size and informs your pregnancy care provider about the fetus's development relative to its gestational age and whether any growth issues are present. The parameters this test measures are CRL (crown-rump length) in frst treatment, BPD (biparietal diameter), HC (head circumference), AC (abdominal circumference), and FL (femur length).
2. Fundal Height Measurement
During pregnancy, a fundal height measurement aids in estimating the size of the fetus. Generally speaking, the measurement is the distance, in cm, between the apex of the uterus and the pubic bone, and the fundal height is often expected to be within three cm of the number of weeks of pregnancy after week 24. A fundal height that is either higher or lower than anticipated, or that fluctuates more quickly or more slowly than anticipated, might indicate the possibility of a problem in fetal development. This method may give erroneous estimations in multiple pregnancies, pregnancy with fibroid, oligohydramnios (insufficient amniotic fluid), and polyhydramnios (an excess of amniotic fluid).
3. Doppler Blood Flow Studies
A Doppler ultrasound creates pictures of blood flowing through your circulatory system and fetal vessels, and the pictures display the blood’s path and velocity as it passes through your veins or arteries. As a result, a Doppler ultrasound’s findings assist medical professionals in determining whether blood flow in the arteries is in an optimal way
or not. There are multiple Doppler ultrasounds called Color Doppler, Spectral Doppler, Duplex ultrasound, Power Doppler, and Transcranial Doppler ultrasound. The fetus receives nutrients from the mother’s blood, so if the findings show that there is any Doppler abnormality in fetal or maternal vessels by increasing the surveillance we can keep the fetus safe.
4. Amniotic Fluid Volume Assessment
Each time you have an ultrasound, the volume of amniotic fluid is measured, a common method to monitor foetal growth! Your fetus is surrounded by amniotic fluid, which aids in the development of your baby's muscles, lungs, and digestive system. You run the risk of early birth and other difficulties if the amniotic fluid is either too high or too low, and it might also indicate a placental or fetal issue.
Final Remarks
To avoid pregnancy complications and to keep the mother and the baby safe, regular fetal growth checks are necessary! Your doctor will prescribe tests in each trimester to ensure the baby is growing normally and the fetus doesn’t have any developmental issues.
To receive the best pregnancy care in a cutting-edge facility, call Medanta and book an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist.






