Gastrosciences



Capsule endoscopy is a medical process that is used to examine the small intestine. During this diagnostic test, the patient is asked to swallow a capsule that has an inbuilt camera. This camera captures endless pictures of the digestive organs, which are displayed on the computer screen.

Endoscopic ultrasound diagnostic test (EUS test) is a combination of endoscopy and ultrasound. It is a procedure performed for clinical assessment of the digestive tract by producing detailed images of the complete digestive tract, chest, and other organs.

Lap Cholecystectomy is one of the minimally invasive techniques practiced to remove gallbladder and gallstones. After the introduction of this new medical technique, surgeons have been able to view the inside of the body better, improvising on the surgical incisions.

An ileostomy is a surgical procedure in which the surgeon opens the abdominal wall to bring the end or loop of the small intestine out onto the surface of the skin. This procedure is necessary when the large intestine is not capable of safely releasing the intestinal waste.

Gastrointestinal bleeding is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention due to its potentially life-threatening nature. In such critical situations, therapeutic endoscopy plays a crucial role in diagnosis, localisation, and treatment. In gastrointеstinal bleeding, blood appear іn thе dіgеstive systеm. Numеrous condіtіons, such as pеptic ulcеrs, gastrіtіs, varices, and cancer, can cause this blееding. Common symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding include hematemesis (vomiting blood), melena (dark, tarry stools), and hematochezia (bright red blood in stools).

Ulcers are painful sores in the stomach or small intestine that develop when the stomach acid damages the line of the digestive tract. The most common symptom of a stomach ulcer is a burning or gnawing pain.

Gastroesophageal reflux disease is chronic digestive disease which occurs when stomach acid flows back into food pipe.
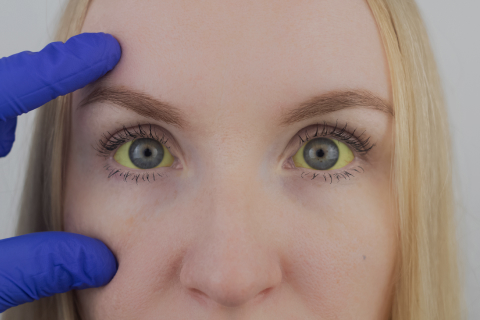
Gilbert’s Syndrome (GS) is an inherent disease of the liver in which the liver enzyme (the protein molecule) cannot properly process bilirubin, which leads to yellowing of eyes and skin.



















